Wood Smoke Emissions Effects on Host Pulmonary Immune Defense, Judith T. Zelikoff, Ph.D. In a laboratory study at New York University, animals exposed to wood smoke immediately had a 25% decrease in the lungs' ability to clear bacteria, and after just 1.5 to 2.5 hours, had decreases of 23% to 61% in lung function.
Contagious Disease:
Wood Smoke exposure is a risk factor for Meningococcal Meningitis . "Exposure to smoke from cooking fires or close contact with a case puts people at risk of contracting meningococcal meningitis. "
Wood smoke may be a risk factor for Sarcoidosis.
Smoke exposure causes thinner skin. Wrinkles Also see Dioxin IllnessSmoke Related Death and Disease:
Cell Damage April 7, 2003, Los Angeles Times, by Gary Polakovic The findings also are the first to show that very tiny particles travel beyond the lungs and bloodstream to penetrate deep inside cells. The pollutant accumulates within a critical component that powers the cell and maintains its function. Damage to that cellular component is known to lead to an assortment of diseases.
Journal Environmental Health Perspectives, a publication of the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, and is currently available on the journal's Internet home page.
Burn Injury caused by open burning.
Coal Smoke Causes Genetic Mutation
Wood Smoke Causes Significant DNA Damage Toxicology: 2000 "Wood smoke particles generate free radicals and cause lipid peroxidation, DNA damage, NFkappaB activation and TNF-alpha release in macrophages"
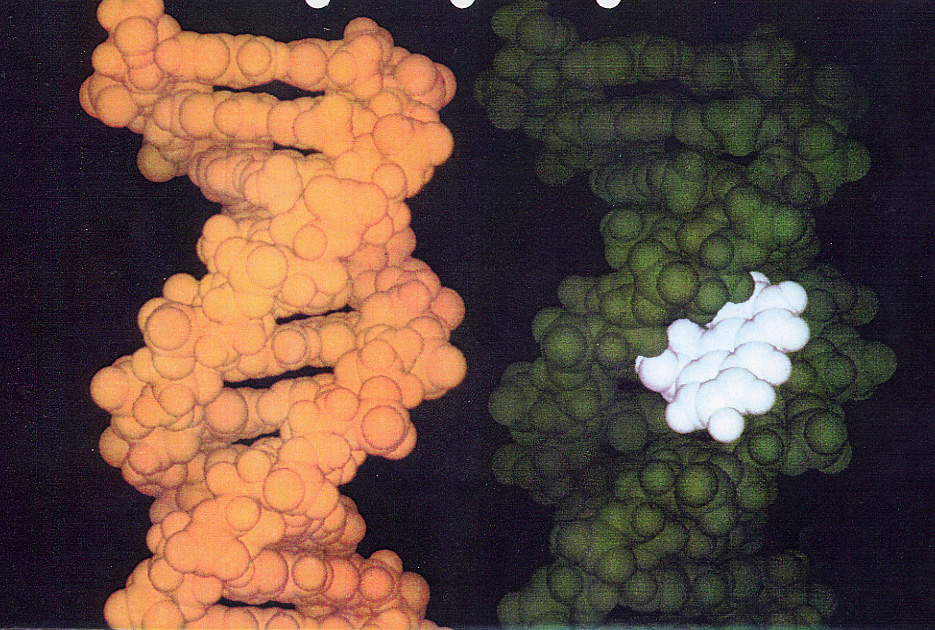
EPA picture simulating how Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, (PAH) adhere to DNA ( see the white patch).